Abstract
Analytical data showed that the crude protein and crude fiber contains of maple seed whole fruit body are 26.44, 22.99% and 8.04, 10.33% respectively. Maple seed characterized with especially high level of Mg due to high contend of chlorophyll in seed. Maple seed has balanced essential amino-acid composition and relatively high level of methionine and tryptophan compared with soybean seed. The storage protein composition of maple tree is relatively simple and characterized with high level of 11S globulin which has high methionine contend. The storage protein consists of 30% of albumin which has balanced amino-acid composition.
Introduction
The great leader president
"Research work on protein food should be efficient." (
Maple sugar and maple syrup have long been important non-timber forest products in North America. During the 18th and 19th centuries, maple sugar was an inexpensive substitute for cane sugar and a cash crop that fit into the work schedule of the northern farmer. Maple syrup replaced maple sugar as the mainstay of the industry at the end of the 19th century as increasingly cheaper cane sugar and other sweeteners undercut the sugar market. Although the genus Acer is widely distributed throughout temperate North America and Eurasia, only eastern North America possesses the appropriate species, i.e., the sugar maple (Acer saccharum Marshall), the black maple (Acer nigrum Michx. f.), and to a lesser extent the red maple (Acer rubrum L.), and the requisite climate, i.e., cold nights
(below 0℃) alternating with warm days (above 0℃), that generates a copious flow of sweet sap (Tyree, 1983; Bertrand, 1995). Recently it was revealed that maple tree (Acer saccharinum) has high productivity of maple nut which mature and fall down in early spring days and it's crude protein content comparable with that of legumes, so it will be potential protein resource for feeding fish and animals. The present study represents a result of analysis of nutritional content and seed protein forming characteristic of maple nut.
1. Materials and methods
-Collection of sample for analysis.
Samples for analysis of nutritional content and seed storage protein forming characteristics were collected from matured and wind dried maple nut.
-analysis of crude protein, oil, fiber and ash contents were analyzed by using Keldal, Socsred, and photo-spectrum methods.
-analysis of seed protein composition and seed storage protein forming characteristics were carried out by using electrophoresis and light-microscopic methods.
2. Results and discussion
1) Nutritional content
The nutritional content of maple nut and it's seed was analyzed.
Maple seed contains 15% of moisture, 26.44% of crude protein, 2.69% of crude oil, 1.86% of crude fiber, 49.83% of non-nitrogen extract, and 4.18% of crude ash respectively. Maple nut contains 15% of moisture, 22.99 %of crude protein, 0.93% of crude oil, 10.34% of crude fiber, 44.87% of non-nitrogen extract, and 5.87% of crude ash respectively.
As shown in this analytic data, crude protein content of maple seed is lower then that of soybean seed but it is quite comparable with that of other representatives of legume family and non-nitrogen extract content is very similar with legume. From these result maple nut can be considered one of the potential protein resources for fish and animal feeding.
2). Vitamin and amino-acid content of maple nut
Vitamin and amino-acid content of maple nut and its' seed was analyzed.
Maple nut contains acceptable amount of vitamins which play important role in animal nutrition. Especially maple nut is characterized with high content of β-carotene.
Also maple nut has balanced amino-acid content.
3) Seed protein composition and seed storage protein forming characteristics
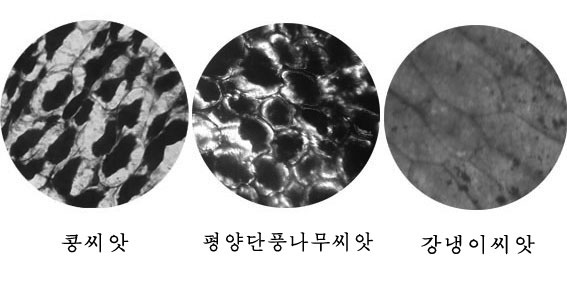
From previous data maple seed has crud similar protein content with legume seed. In pic.1 form of seed storage protein particles was shown with soybean and maize seed as control.
Pic.1. form of seed storage protein particles
As shown in pic.1 the size of cell of storage tissue is similar with that of soybean seed but a little smaller than that of maize and size and distribution density of storage protein particles of maple seed is also comparable with that of soybean seed.
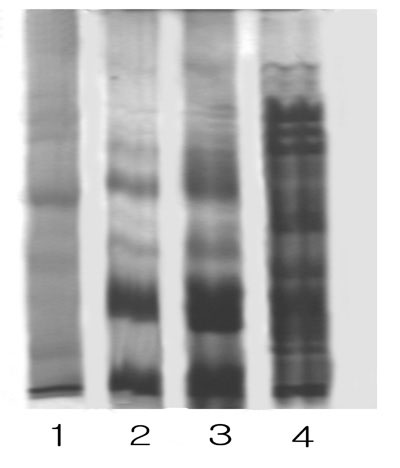
The seed storage protein composition can be one of the characteristics in evaluation of protein quality so that the subunit composition of maple seed protein was illustrated by using SDS-electrophoresis (Pic. 2).
Pic. 2. SDS-electrophoretogram of maple seed protein according several period of mature.
(1-maple nut of the 15 days after falling of flower, 2-maple nut of the 30 days after falling of flower, 3-maple nut of the 45 days after falling of flower, 4-soybean seed).
As shown in pic. 1 the composition of seed storage protein is changed quantitatively according to maturing period.
The maple seed storage protein composition is characterized with high content of 7S-like protein which has high amount of methionine. This result is quite explainable when it compared with the analytic data of amino-acid content.
Among maple seed protein composition main (70%) component was globulin and others were albumin.
Summary
1. Maple seed contain 15% of moisture, 26.44%of crude protein, 2.69% of crude oil, 1.86% of crude fiber, 49.83% of non-nitrogen extract, and 4.18% of crude ash respectively. Maple nut contain 15% of moisture, 22.99 %of crude protein, 0.93% of crude oil, 10.34% of crude fiber, 44.87% of non-nitrogen extract, and 5.87% of crude ash respectively.
2. Maple nut contains acceptable amount of vitamins which play important role in animal nutrition. Especially maple nut is characterized with high content of β-carotene.
3. The maple seed storage protein composition is characterized with high content of 7S-like protein which has high amount of methionine.